- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2024-10-02 Origin: Site











The selection between lead screws and ball screws hinges on critical distinctions in their structure,operational principles,and performance characteristics.While both convert rotary motion into linear motion,lead screws rely on sliding friction between the screw and nut,inherently limiting speed and efficiency but offering self-locking capability.Ball screws,conversely,utilize recirculating ball bearings to achieve rolling friction,enabling significantly higher efficiency,precision,and speed capacity,albeit without inherent self-locking.Understanding these core differences—spanning materials,transmission efficiency,precision,backlash control,and application suitability—is essential for optimal mechanical system design.
The lead screw comprises a screw rod and a nut.The ball screw comprises a screw rod,a ball nut,and balls.During operation,the leadscrew utilizes direct sliding friction between the screw rod and nut.The ball screw utilizes balls moving within the ballnut during operation;they constitute rolling friction.
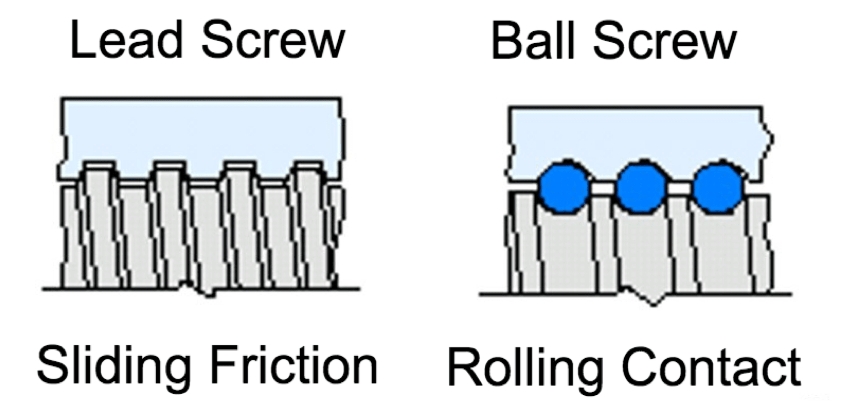
Lead screws are typically manufactured from S45C or SS303/SS304 materials.Lead nuts can be made of polymers or copper alloys.Ball screws generally utilize GCr15 or 9Cr18 materials.Since ball screws operate with rolling friction and exhibit a low friction coefficient,both ball screw shaft/ballnut and steel balls can be manufactured from identical materials to ensure sufficient structural integrity throughout the assembly.
As can be seen from below figure,the coefficient of rolling friction is significantly lower than that of sliding friction.The friction coefficient of sliding lead screws ranges between 0.1–0.3,while that of ball screws ranges from 0.003 to 0.01.
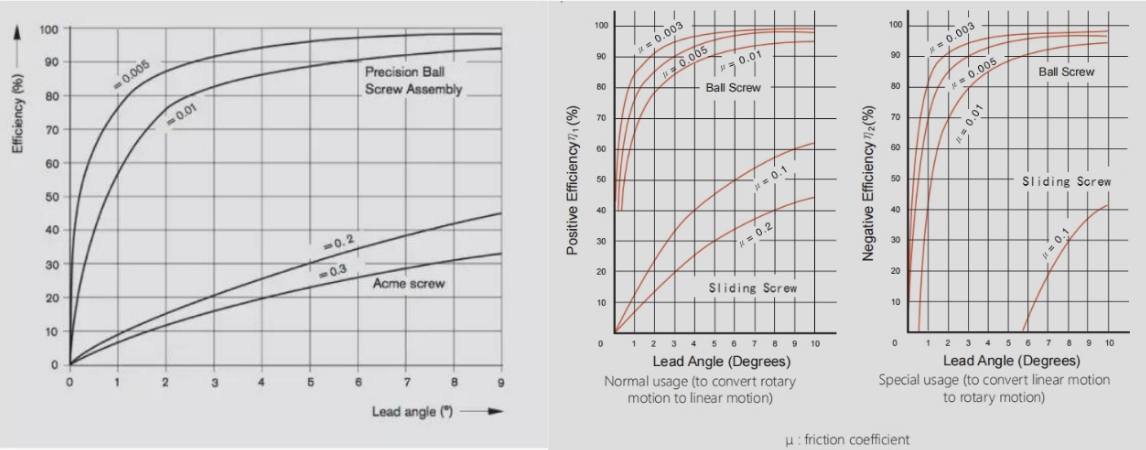
According to the law of energy conservation,lead screws exhibit low transmission efficiency.During operation,friction generates substantial heat,particularly at high speeds,where significant heat is transferred to the screw rod and nut.Under these conditions,the copper alloy nut experiences thermal degradation,and plastic nuts are especially prone to damage due to overheating.Consequently,leadscrews are unsuitable for high-speed applications,with a maximum rotational speed typically not exceeding 3000 PRM.In contrast,ball screws feature high transmission efficiency and generate minimal heat,enabling speeds of up to 10000 RPM.
Theory shows that when the efficiency of a screw drive exceeds 50%,the screw does not require self-locking capability.When the efficiency is below 35%,the screw exhibits self-locking properties.In simple terms,ball screws lack self-locking capability,while lead screws possess a certain degree of self-locking capability.In particular,the larger the diameter of the screw and the smaller the lead,the smaller the lead angle formed,and the stronger the self-locking capability.
The self-locking capability of leadscrews,especially for vertical applications,offers a significant advantage over ball screws.For vertical applications,after the motor at the input end of the ball screw is powered off,the ball screw cannot self-lock and requires additional structural components or devices to prevent the ballnut from slipping and causing hazards.Many motors now come with built-in brake modules that can hold the motor shaft in place even when power is cut off,preventing the motor shaft from rotating and providing protection.However, the torque provided by the brake is limited,and the appropriate model should be selected based on requirements.For vertically mounted lead screws with self-locking properties,the lead nut will not slip on its own.Even if the motor is powered off or the physical connection to the power input end is disconnected,the nut will not slip.The safety is highly reliable.
Ball screws primarily employ two processing methods: grinding and cold rolling.
Grinding:This method uses grinding wheels to precisely grind the required threads.Ball screws produced using this method typically achieve precision levels of C3 or C5,with the highest achievable level being C0.
Cold rolling:This process uses a threading wheel to form the required thread shape by squeezing a round bar.Ball screws produced using this process typically have a precision grade of C7.
Ball screw lead accuracy is divided into six grades from highest to lowest:
C0 (±0.0035 mm/300 mm),C1 (±0.05 mm/300 mm), C3 (±0.08 mm/300 mm), C5 (±0.018 mm/300 mm), C7 (±0.05 mm/300 mm),C10 (±0.21 mm/300 mm).
Regardless of the manufacturing process used to produce the ballscrew shaft,the ball nuts are all manufactured using a grinding process.In terms of cost and delivery time,cold-rolled ball screws are preferred when meeting the required precision,as they are cost-effective and have a shorter production cycle.
Lead screws primarily use three manufacturing processes: rolling,turning,and grinding.
Rolling can achieve a harder surface and better surface finish for the threads.
Grinding achieves the highest precision,followed by turning,while rolled lead screws have the lowest precision.
For lead screws,rolled precision is generally ±90 μm/300 mm,turning precision is generally ±50 μm/300 mm,and ground precision is generally ±12.5 μm/300 mm.
Lead screws use sliding friction transmission,with the clearance between the lead screw and nut typically ranging from 0.02 mm to 0.25 mm.For lead screws with no clearance requirements,a spring structure can be added in the middle.The spring tightens the nuts on both sides of the lead screw shaft in both directions,ensuring full contact between nuts and the lead screw shaft.The drawback is poor axial rigidity.If greater rigidity is required,the spring force must be increased,which significantly increases friction,leading to higher motor operating torque,accelerated wear,and reduced lead screw lifespan.
Ball screws can be selected with different axial clearances and preload magnitudes as needed.Clearances can range from 0 to 0.05,or 0 clearance,0 preload and 0 clearance,light preload,medium preload,or heavy preload.Preload adjustment methods include modifying the ball diameter or using preload shims to adjust the clearance and preload.
Lead screws are suitable for applications that require light weight,low speed,harsh operating conditions,and self-locking requirements.Examples include manual water gates and vise clamps.Ball screws are suitable for applications that require high precision,smooth movement,high efficiency,long-term continuous operation,or high-speed movement.Examples include medical equipment,3D printing equipment,and semiconductor equipment.